
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) is one of the most important products of cellulose ethers, which are formed by natural cellulose modification as a kind of cellulose derivate with an ether structure.
Due to the fact that the acid form of CMC has poor water solubility, it is usually preserved as sodium carboxymethylcellulose, which is widely used in many industries and regarded as monosodium glutamate in industry.
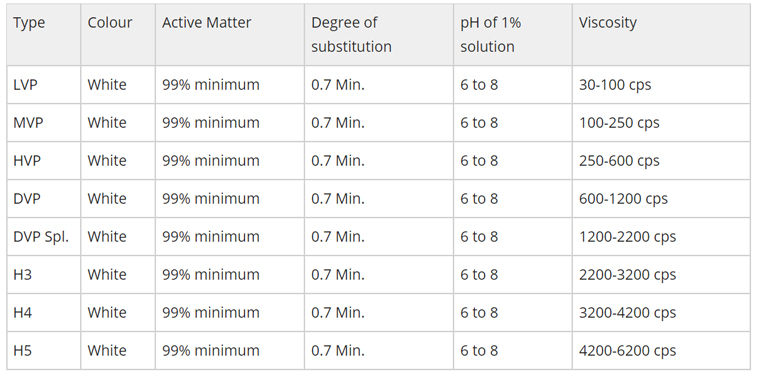
Sodium CMC is a versatile hydrocolloid and is soluble in both warm and
cold water and is insoluble in organic solvents. Sodium CMC is available in various grades of viscosity.
| TESTS | Specifications |
| Description | White or almost granular powder, odourless or almost white, hygroscopic |
| Solubility | Practically insoluble in acetone, in ethanol, in ether and in toluene. It is dispersed in water forming a colloidal solution. |
| Identification | A. Blue cotton-like precipitate with copper
sulphate solution. B. No precipate on boiling C. Shows reaction of sodium |
| Appearance of solution | Not more opalewscent than opalescence standard OS4 and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Ys6 |
| pH | 6.0 to 8.0 |
| Apparent viscosity | 75.0% to 140% of declared value |
| Arsenic | Maximum 1 ppm |
| Heavy metals | Maximum 20 ppm |
| Chlorides | Maximum 0.25 % |
| Sulphated ash | 20.0 to 33.3% |
| Loss on drying(%) 1g. 105⁰ C | Maximum 10% |
| Assay (% sodium on dried basis) | 6.5 to 10.8% sodium |